

At the end of the second trial, inform the subject that (s)he will be asked to recall these words again by saying, “ I will ask you to recall those words again at the end of the test.” Try to remember and tell me as many words as you can, including words you said the first time.” Put a check in the allocated space for each word the subject recalls after the second trial. When the subject indicates that (s)he has finished (has recalled all words), or can recall no more words, read the list a second time with the following instructions: “ I am going to read the same list for a second time.
It doesn’t matter in what order you say them.” Mark a check in the allocated space for each word the subject produces on this first trial. When I am through, tell me as many words as you can remember. I am going to read a list of words that you will have to remember now and later on. Copyright © 2008 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.Read a list of 5 words at a rate of 1 word per second, giving the following instructions: “ This is a memory test. The results are suggestive of a breakdown in the maintenance of information in working memory in terms of chunking it appears that ecstasy/polydrug users are as able as non-ecstasy users to form memory ‘chunks’ from the items, but that such chunks are not retained as effectively. Copyright © 2008 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.The results of the present study provide further support for updating deficits in ecstasy-polydrug users.
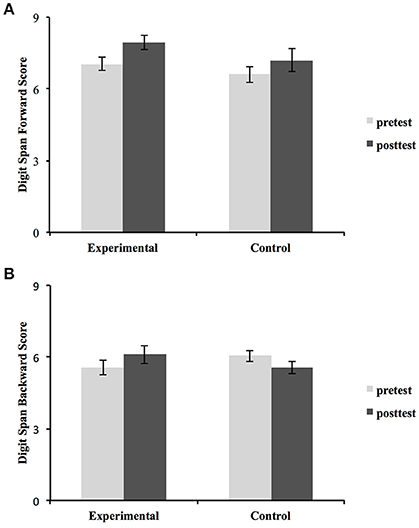
#BACKWARD DIGIT SPAN TEST SCORE SERIAL#
Three of these were due to impaired recall of earlier serial positions.ConclusionsThe results of the present study provide further support for updating deficits in ecstasy-polydrug users. Three of these were due to impaired recall of earlier serial positions.Ecstasy-polydrug users were impaired in four out of the six sub-sample analyses. The digit span backwards (DSB) is the most commonly used test in clinical neuropsychology to assess working memory capacity. Participants were categorised according to letter and spatial span (four, five or six), producing six sub-samples for analysis.ResultsEcstasy-polydrug users were impaired in four out of the six sub-sample analyses. Participants were categorised according to letter and spatial span (four, five or six), producing six sub-samples for analysis.Seventy-three ecstasy/polydrug users and seventy-three non-ecstasy users completed tasks of verbal and spatial memory running memory, recalling the most recent items, in lists of varying and unknown length. The present study sought to determine if ecstasy-related deficits in memory updating are related to serial position of items presented, or length of the list of items.MethodSeventy-three ecstasy/polydrug users and seventy-three non-ecstasy users completed tasks of verbal and spatial memory running memory, recalling the most recent items, in lists of varying and unknown length. Less is known about the precise nature of such deficits. The updating component appears to be particularly susceptible. The present study sought to determine if ecstasy-related deficits in memory updating are related to serial position of items presented, or length of the list of items.Research shows that users of ecstasy (MDMA) exhibit deficits in executive processes. A final total score of 26 and above is considered normal. The updating component appears to be particularly susceptible. The MoCA is a cognitive test used for screening mild cognitive impairment. AimsResearch shows that users of ecstasy (MDMA) exhibit deficits in executive processes.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
